Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Care
Introduction:
We shall go into the world of diabetes in this blog article, a chronic illness that affects millions of individuals worldwide. We will examine this widespread ailment's aetiology, manifestations, symptoms, and available treatments in order to better understand it.
What is Diabetes?
High blood sugar levels brought on by a lack of insulin or by increasing insulin resistance characterize diabetes, a metabolic disorder. By making it easier for cells to absorb glucose for energy, the pancreatic hormone insulin controls blood sugar. When this process is disrupted, diabetes occurs.
Diabetes Risk Factors and Causes:
The following things can increase your risk of developing diabetes:
- Genetic Predisposition: Having diabetes in the family raises the likelihood of getting the disease.
- Lifestyle Decisions: Sedentary behaviour, a sedentary diet, and a lack of physical activity all contribute significantly to the development of diabetes.
- Obesity: An elevated risk of type 2 diabetes is tightly correlated with excess body weight.
- Gestational Factors: Pregnancy can trigger gestational diabetes, affecting blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
Varieties of Diabetes
- When the immune system attacks and kills the pancreatic cells that make insulin, type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune condition, results. People with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy.
- The most prevalent type of diabetes, type 2, is brought on when the body either stops producing enough insulin or produces it insufficiently. Lifestyle modifications, medication, and sometimes insulin therapy are used for management.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes affects blood sugar levels. Although it normally goes away after giving birth, it raises the possibility of type 2 diabetes in the future.
Diabetes Symptoms, Signs, and Effects:
Knowing the symptoms and indicators of diabetes is crucial for both early detection and management of the condition:
- increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Blurred vision and slow wound healing
Diabetes can have long-term effect such as kidney disease, nerve damage, cardiovascular disease, vision problems, and others.
Diabetes Management and Care:
Proper diabetes management is essential for controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications:
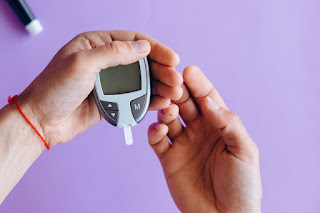
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps individuals make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and overall diabetes management.
.jpg)
Medication and Insulin Therapy: Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, medication and insulin therapy may be advised to regulate blood sugar levels.

Healthy Eating: A balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense cereals, lean meats, fruits, and vegetables is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
How Does Diabetes Occur?
Complex physiological pathways lead to diabetes:
- Production and Use of Insulin: The pancreas produces insulin, which enables cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream.
- Insulin Resistance and Impaired Glucose Regulation: Type 2 diabetics' cells become resistant to insulin, which causes blood sugar levels to rise. Insulin-producing cells are attacked by the immune system in persons with type 1 diabetes, resulting in decreased or nonexistent insulin production.
- Effects of Elevated Sugar Levels: Over time, chronically high blood sugar levels can harm kidneys, neurons, the heart, blood vessels, and the eyes.
Conclusion:
Diabetes must be managed and cared for continuously throughout one's lifetime. By understanding its causes, types, symptoms, and care options, individuals can take proactive steps towards better diabetes control and overall well-being. Keep in mind to speak with medical specialists for personalized guidance and care suited to your unique need. Stay informed, embrace a healthy lifestyle, and prioritize regular medical check-ups to effectively manage diabetes and live a fulfilling life.

.jpg)




0 Comments